All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Exploration Geophysicist: Occupations In Albe...
- – Geophysicist Job Description: Salary, Duties...
- – Geophysical Surveys: Definition & Methods in...
- – Geophysicist, Exploration - Job Description...
- – Geophysical Survey: Plotting Buried Traces ...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in Kardinya A...
- – Importance Of Geophysical Surveys — Method...
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Myaree Wes...
- – Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Mt Ri...
- – An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techni...
Exploration Geophysicist: Occupations In Alberta in Embleton Aus 2022
What is the task description of a Geophysicist? What are the responsibilities and obligations of a Geophysicist? What does a Geophysicist do? A geophysicist research studies physical elements of the earth and utilizes intricate devices to collect data on earthquakes and seismic waves, which move through and around the earth. The best markets for geophysicists are the mining and oil industries, as they play a substantial part in the acquisition of natural resources.
This Geophysicist task description example consists of the list of crucial Geophysicist responsibilities and obligations as shown listed below. It can be modified to fit the specific Geophysicist profile you're attempting to fill as an employer or task candidate.
Career chances differ commonly across a variety of fields including geophysical data, climate modelling, engineering geology, hydrology, mining, environmental consulting, natural resources expedition, farming, and others. There are numerous profession courses that can integrate your scholastic backgrounds, abilities, and experience with your various interests. Check out through the task titles listed below for concepts.
Geophysicist Job Description: Salary, Duties, & More in Beldon Australia 2023
Visit the National Occupational Category website to research study standard requirements and duties of tasks in your field.
Geophysics plays in important role in numerous elements of civil engineering, petroleum engineering, mechanical engineering, and mining engineering, as well as mathematics, physics, geology, chemistry, hydrology, and computer technology. For that reason, trainees in other majors may think about a minor in geophysical engineering. The core courses needed for a minor are: GPGN229, Mathematical Geophysics (3.
0 credits) GPGN329, Physics of the Earth II (3. 0 credits) Students might please the staying 5 hours with a combination of other geophysics courses, as well as courses in geology, mathematics, or computer system science, depending on the trainee's major.
Geophysical Surveys: Definition & Methods in Koondoola Oz 2023
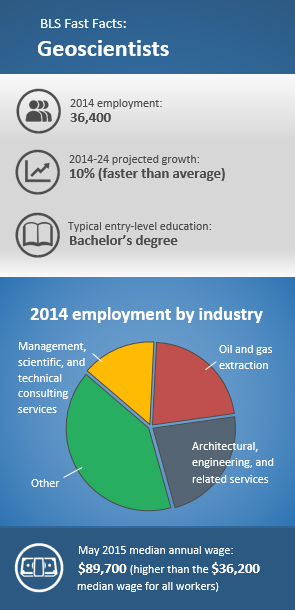
The salary level of geophysicists can vary depending on aspects such as their level of education, their level of experience, where they work, and numerous others. Some geophysicists may likewise spend long periods of time working in little groups in remote places.
When conducting fieldwork, the working hours of geophysicists can be long and consist of evenings, weekends and holidays. To become a qualified geophysicist, you require to posses a certain set of abilities and characteristic. These abilities and characteristics will enable you to efficiently perform the duties of your task, in addition to keep a favorable attitude towards your work.
Geophysicist, Exploration - Job Descriptions in Wexcombe Oz 2022
Colleges and universities Federal, provincial/state government departments Oil, gas and mining companies Non-profit organizations Geological and geophysical consulting business Public and personal research study companies Our task board below has "Geophysicist" posts in Canada, the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia, when available:.
Our data suggests that the greatest spend for a Geophysicist is $165k/ year Our data suggests that the most affordable pay for a Geophysicist is $55k/ year Increasing your pay as a Geophysicist is possible in different methods. Modification of company: Think about a profession move to a new company that wants to pay greater for your skills.
Managing Experience: If you are a Geophysicist that manages more junior Geophysicists, this experience can increase the possibility to earn more.
Geophysical Survey: Plotting Buried Traces Of Human Activity in Palmyra Oz 2023
Physics of the Earth and its vicinity Age of the sea floor. Much of the dating details comes from magnetic abnormalities. Geophysics () is a topic of natural science worried about the physical processes and physical homes of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and using quantitative methods for their analysis.
The term geophysics classically refers to strong earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, electromagnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its characteristics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock development. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure researchers use a more comprehensive definition that includes the water cycle consisting of snow and ice; fluid characteristics of the oceans and the environment; electrical energy and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and comparable problems connected with the Moon and other worlds. , which includes other planetary bodies.
The gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun offers rise to 2 high tides and two low tides every lunar day, or every 24 hr and 50 minutes. For that reason, there is a space of 12 hours and 25 minutes in between every high tide and between every low tide. Gravitational forces make rocks push down on deeper rocks, increasing their density as the depth boosts.
How To Become A Geophysicist in Kardinya Aus 2021
The geoid would be the global mean sea level if the oceans were in balance and might be extended through the continents (such as with very narrow canals).
The main sources of heat are the primitive heat and radioactivity, although there are also contributions from phase transitions. Heat is mostly reached the surface by thermal convection, although there are 2 thermal limit layers the coremantle border and the lithosphere in which heat is transported by conduction. Some heat is brought up from the bottom of the mantle by mantle plumes. 2 1013 W, and it is a potential source of geothermal energy. Illustration of the deformations of a block by body waves and surface waves (see seismic wave). Seismic waves are vibrations that take a trip through the Earth's interior or along its surface. The entire Earth can also oscillate in types that are called regular modes or totally free oscillations of the Earth. If the waves come from a localized source such as an earthquake or explosion, measurements at more than one location can be used to locate the source. The locations of earthquakes provide info on plate tectonics and mantle convection.
Reflections recorded using Reflection Seismology can provide a wealth of info on the structure of the earth up to numerous kilometers deep and are utilized to increase our understanding of the geology along with to explore for oil and gas. Modifications in the travel instructions, called refraction, can be utilized to infer the deep structure of the Earth. Understanding their systems, which depend upon the kind of earthquake (e. g., intraplate or deep focus), can result in much better price quotes of earthquake risk and improvements in earthquake engineering. Although we primarily see electrical energy throughout thunderstorms, there is always a down electrical field near the surface that averages 120 volts per meter. An existing of about 1800 amperes circulations in the global circuit. It streams downward from the ionosphere over the majority of the Earth and back upwards through thunderstorms. The flow appears by lightning below the clouds and sprites above. A range of electric methods are utilized in geophysical survey. Some measure spontaneous possible, a potential that emerges in the ground since of manufactured or natural disruptions.
Importance Of Geophysical Surveys — Methods And Uses in Burswood Australia 2022
They have 2 causes: electromagnetic induction by the time-varying, external-origin geomagnetic field and movement of performing bodies (such as seawater) across the Earth's long-term electromagnetic field. The circulation of telluric existing density can be utilized to spot variations in electrical resistivity of underground structures. Geophysicists can likewise provide the electrical current themselves (see induced polarization and electrical resistivity tomography).
Dawn chorus is believed to be brought on by high-energy electrons that get captured in the Van Allen radiation belt. Whistlers are produced by lightning strikes. Hiss may be generated by both. Electro-magnetic waves might also be created by earthquakes (see seismo-electromagnetics). In the highly conductive liquid iron of the outer core, electromagnetic fields are produced by electric currents through electro-magnetic induction.
In the core, they most likely have little observable impact on the Earth's magnetic field, but slower waves such as magnetic Rossby waves may be one source of geomagnetic secular variation. Electromagnetic approaches that are used for geophysical survey include transient electromagnetics, magnetotellurics, surface area nuclear magnetic resonance and electro-magnetic seabed logging. , powering the geodynamo and plate tectonics.
What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Myaree Western Australia 2022
Radioactive elements are utilized for radiometric dating, the primary technique for developing an outright time scale in geochronology. Unsteady isotopes decay at predictable rates, and the decay rates of different isotopes cover numerous orders of magnitude, so radioactive decay can be used to accurately date both current occasions and occasions in past geologic eras.
Fluid motions occur in the magnetosphere, environment, ocean, mantle and core. Even the mantle, though it has a huge viscosity, streams like a fluid over long time periods. This flow is shown in phenomena such as isostasy, post-glacial rebound and mantle plumes. The mantle flow drives plate tectonics and the circulation in the Earth's core drives the geodynamo.
Waves and other phenomena in the magnetosphere can be modeled using magnetohydrodynamics. The physical homes of minerals should be understood to infer the composition of the Earth's interior from seismology, the geothermal gradient and other sources of details. Mineral physicists study the flexible homes of minerals; their high-pressure phase diagrams, melting points and formulas of state at high pressure; and the rheological properties of rocks, or their ability to circulation. The viscosity of rocks is affected by temperature and pressure, and in turn, identifies the rates at which tectonic plates move. Water is an extremely complex substance and its special homes are necessary for life. Its physical homes form the hydrosphere and are a vital part of the water cycle and climate.
Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Mt Richon Australia 2022
The Earth is roughly spherical, but it bulges towards the Equator, so it is approximately in the shape of an ellipsoid (see Earth ellipsoid). This bulge is due to its rotation and is almost consistent with an Earth in hydrostatic equilibrium. The detailed shape of the Earth, however, is also affected by the distribution of continents and ocean basins, and to some extent by the characteristics of the plates.
Proof from seismology, heat circulation at the surface, and mineral physics is combined with the Earth's mass and moment of inertia to presume designs of the Earth's interior its structure, density, temperature level, pressure. The Earth's mean specific gravity (5. 515) is far greater than the common particular gravity of rocks at the surface (2.
3), suggesting that the deeper product is denser. This is also implied by its low moment of inertia (0. 33 M R2, compared to 0. 4 M R2 for a sphere of constant density). Some of the density increase is compression under the huge pressures inside the Earth.
An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techniques For ... in Gwelup Australia 2020
The conclusion is that pressure alone can not account for the increase in density. Rather, we know that the Earth's core is composed of an alloy of iron and other minerals. Restorations of seismic waves in the deep interior of the Earth show that there are no S-waves in the outer core.
The external core is liquid, and the movement of this extremely conductive fluid produces the Earth's field. Earth's inner core, nevertheless, is strong because of the huge pressure. Reconstruction of seismic reflections in the deep interior indicates some major discontinuities in seismic speeds that demarcate the major zones of the Earth: inner core, external core, mantle, lithosphere and crust.
Table of Contents
- – Exploration Geophysicist: Occupations In Albe...
- – Geophysicist Job Description: Salary, Duties...
- – Geophysical Surveys: Definition & Methods in...
- – Geophysicist, Exploration - Job Description...
- – Geophysical Survey: Plotting Buried Traces ...
- – How To Become A Geophysicist in Kardinya A...
- – Importance Of Geophysical Surveys — Method...
- – What Does A Geophysicist Do? in Myaree Wes...
- – Gravity Geophysical Survey Method in Mt Ri...
- – An Assessment Of Geophysical Survey Techni...
Latest Posts
Geophysicist Jobs in North Perth Australia 2021
Geophysical Survey Definition in Warnbro Western Australia 2021
What Is Geophysics? in Carlisle Australia 2020
More
Latest Posts
Geophysicist Jobs in North Perth Australia 2021
Geophysical Survey Definition in Warnbro Western Australia 2021
What Is Geophysics? in Carlisle Australia 2020